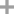
- Chemical Name:Isoflurane
- CAS No.:26675-46-7
- Molecular Formula:C3H2ClF5O
- Molecular Weight:184.493
- Hs Code.:2909191800
- European Community (EC) Number:247-897-7
- ICSC Number:1435
- UNII:CYS9AKD70P
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID3020752
- Nikkaji Number:J2.770G
- Wikipedia:Isoflurane
- Wikidata:Q413918
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C65978
- RXCUI:6026
- Pharos Ligand ID:XUMC5VNDWJVP
- Metabolomics Workbench ID:53234
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL1256
- Mol file:26675-46-7.mol
Synonyms:Ether,1-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl (8CI);1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether;Aerrane;Attane;Compound469;Difluoromethyl 1-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl ether;Forane;Forene;HCFE235da2;IsoFlo;IsoFlo (anesthetic);Isoforine;R-E 235da1;


 F,
F, T
T