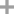
- Chemical Name:Indigo
- CAS No.:482-89-3
- Deprecated CAS:11129-41-2,12000-74-7,12626-73-2,93660-98-1,136797-30-3,210488-46-3,908005-94-7,1131642-59-5,2089217-02-5,2089217-38-7,1131642-59-5,12000-74-7,12626-73-2,136797-30-3,2089217-02-5,2089217-38-7,210488-46-3,908005-94-7,93660-98-1
- Molecular Formula:C16H10N2O2
- Molecular Weight:262.268
- Hs Code.:32041510
- European Community (EC) Number:207-586-9
- NSC Number:8645
- UNII:1G5BK41P4F
- DSSTox Substance ID:DTXSID3026279
- Nikkaji Number:J1.210.939C,J2.292.935F,J5.983H
- Wikipedia:Indigo_dye
- Wikidata:Q422662,Q104967020,Q104389767
- NCI Thesaurus Code:C71644
- ChEMBL ID:CHEMBL599552,CHEMBL35479
- Mol file:482-89-3.mol
Synonyms:(delta-2,2'-biindole)-3,3'-dione;2-(1,3-Dihydro-3-oxo-5-sulpho-2H-indol-2-ylidene)-3- oxoindoline-5-sulphonic acid;Carmine, Indigo;D and C Blue NO. 6;FD and C Blue No. 2;indigo;Indigo Blue;Indigo Blue, Soluble;Indigo Carmine;Indigo Disulfonate;indigotin;Indigotindisulfonate;Indigotindisulfonate Sodium;Indigotindisulfonic Acid;Soluble Indigo Blue


 Xi
Xi